Expressvpn Glossary
Bandwidth
What is bandwidth?
Bandwidth refers to the amount of data that a network can transmit in a fixed amount of time. It measures the volume of information that can be sent over a connection. Bandwidth can be a central factor in determining speed. The higher the bandwidth, the more data can be sent over a given time period, which usually determines how long it takes for a video to load or a file to download.
How does it work?
Data moves across a network in small units called packets. Bandwidth affects how many packets a network can send or receive per second. A connection with greater bandwidth can handle a higher volume of packets at once, facilitating faster data transfers.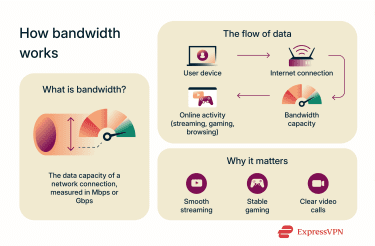 Bandwidth is measured in bits per second (bps). For modern internet connections, the number of bits is quite large, so measurements are typically shown in these units:
Bandwidth is measured in bits per second (bps). For modern internet connections, the number of bits is quite large, so measurements are typically shown in these units:
- Megabits per second (Mbps): One million bits per second. This is the standard for most home internet plans.
- Gigabits per second (Gbps): One billion bits per second. This is common for fiber-optic connections and data centers.
Though related, bandwidth is not the same as throughput. Bandwidth is the theoretical maximum capacity of a connection, while throughput refers to the actual amount of data transferred at a given time. This can be lower than the maximum because of factors like network congestion and hardware limitations.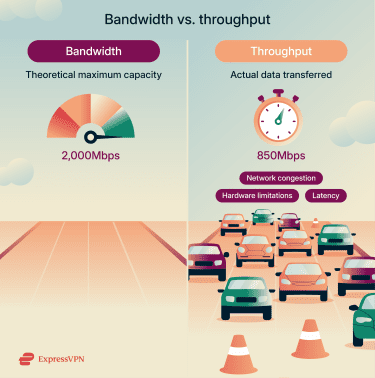
Why is bandwidth important?
The amount of available bandwidth directly affects internet performance and therefore user experience. Sufficient capacity is necessary for data-heavy activities to function without interruption. Without enough bandwidth, users on a network will experience slow loading times, video buffering, and poor connection quality.
Its impact is most noticeable in activities like:
- Streaming and video calls: High-definition video requires a continuous flow of a large amount of data. Limited bandwidth can cause pixelation, buffering, or dropped calls.
- Gaming: Online games need to constantly send and receive data packets. Insufficient bandwidth can lead to lag and a frustrating gameplay experience, even if latency is low.
- Businesses and cloud services: Companies need high-capacity connections to support multiple employees, transfer large files, use video conferencing, and operate cloud-based software.
Where is it used?
Bandwidth is a fundamental concept that applies to all forms of digital communication. It’s a key specification in many real-world applications and technologies.
- Internet service plans: Internet service providers (ISPs) structure their plans around different bandwidth tiers, such as 100Mbps or 1Gbps, for home and business users.
- Mobile networks: The progression from 4G to 5G is largely about increasing bandwidth to support faster data speeds and more connected devices on mobile networks.
- Web hosting: A website’s hosting plan includes a specific amount of bandwidth that determines how much traffic the site can handle before its performance degrades.
Further reading
- How to boost your VPN internet speed
- Types of internet connections
- How to accurately test and improve your VPN speed
FAQ
What is an example of bandwidth?
An internet service plan advertised as “up to 200Mbps” is an example of bandwidth. It means the network connection is designed to handle a maximum data download rate of 200 million bits per second under ideal conditions.
Is higher bandwidth always better?
Not necessarily. Higher bandwidth isn't always better because it’s a measure of data volume, which may not always be necessary. Higher bandwidth generally leads to better performance for most online tasks, but it isn’t the only factor. For real-time applications like online gaming or voice chats, low latency (the time it takes for data to travel to its destination and back) is often more important. A connection can have very high bandwidth but still perform poorly for gaming if it has high latency.
How is bandwidth different from speed?
People often use “speed” and “bandwidth” to mean the same thing, but while related, they can refer to different things. Bandwidth signifies the maximum amount of data that can be transferred over a given time. This often translates directly to the speed at which pages load or files download, but this isn’t always the case, such as when a congested network is working below its maximum capacity. Additionally, speed can also refer to latency, the length of the delay between a data packet leaving its source and reaching its destination. Latency is affected by factors outside bandwidth, such as physical distance and hardware concerns.
How much bandwidth do I need for streaming?
The amount you need depends on the video quality. Streaming services provide their own recommendations, but general guidelines are:
- Standard Definition (SD): 3–5Mbps
- High Definition (HD/1080p): 5–20Mbps
- 4K/Ultra HD (UHD): 15–35Mbps or more
These numbers are per stream, so a household with multiple people streaming at once would need to add those numbers together.
