Expressvpn Glossary
Data mining
What is data mining?
Data mining is the process of using computer programs and mathematical methods to examine large volumes of data in order to extract meaningful information.
How does data mining work?
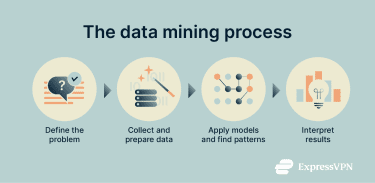
Data mining works by systematically examining large datasets to uncover patterns, trends, and relationships. The process typically involves several key steps:
- Defining the problem: Identifying the research question and determining what insights are needed. This helps ensure the analysis is focused on the right questions and that the results will be meaningful for decision-making.
- Collecting and preparing data: Gathering relevant data from databases, warehouses, or other sources, then cleaning and organizing it. Preparing the data removes errors, duplicates, and inconsistencies, helping to ensure the analysis is accurate and reliable.
- Building models and mining patterns: Applying various data mining techniques and tools to analyze the data.
- Evaluating and interpreting results: Assessing the model’s findings to ensure that they’re valid, useful, and understandable.
Data mining techniques and tools
Here are the key data mining techniques:
- Classification: Grouping data into predefined categories based on shared characteristics.
- Clustering: Identifying groups of similar data points without predefined labels.
- Regression: Predicting numerical outcomes based on input variables.
- Association rules: Discovering relationships between items or events.
- Decision trees: Representing decisions and their possible outcomes in a tree-like structure to classify data or make predictions.
- K-nearest neighbor: Assigning categories to data points based on how close they are to other points.
- Neural networks: Modeling complex patterns in data by mimicking the structure and connections of the human brain.
- Predictive analytics: Using past data to forecast future trends or outcomes.
Some popular data mining tools include:
- RapidMiner: A data mining platform capable of managing the entire data analysis workflow. It excels at predictive analytics.
- WEKA: A toolkit with extensive machine learning capabilities and a variety of classification methods. It’s popular for research and teaching.
- Orange: A data mining platform with interactive visual workflows that make it easy to explore, prepare, and interpret data.
- KNIME: A data mining platform with modular workflows that excels at preprocessing, integrative analysis, and combining multiple machine learning methods.
Data mining vs. data analysis
Both data analysis and data mining involve examining data to uncover insights, but they differ in approach and purpose.
Data analysis focuses on interpreting data to answer a specific question or solve a known problem. For example, a company might analyze last quarter’s sales data to understand why a particular product underperformed.
In contrast, data mining explores large datasets more broadly to find hidden patterns, trends, and relationships that may not be immediately obvious. For instance, the same company could use data mining to discover that customers who buy a certain product are also likely to purchase another, revealing opportunities for cross-selling or targeted promotions.
Why is data mining important?
Data mining is important because it turns raw data into actionable intelligence. This helps businesses and researchers explain underlying causes, understand complex processes, and identify opportunities that would otherwise remain hidden. It also enhances the ability to predict future outcomes, supporting better planning and more informed decisions throughout an organization.
Where is data mining used?
Data mining is applied across many industries and organizational functions. Here are some key applications:
- Fraud detection in finance: Identifying unusual transactions and anomalies to prevent fraud or mismanagement.
- Customer behavior and market analysis: Analyzing purchasing patterns and demographics to optimize campaigns, promotions, and cross-selling.
- Healthcare research and diagnostics: Examining patient data and medical imaging to support diagnosis, treatment planning, and trend analysis.
- Cybersecurity and anomaly detection: Monitoring networks and systems to detect unusual activity, potential breaches, or other security threats.
- Human resources and workforce management: Examining employee data to understand trends in performance, satisfaction, retention, and training needs.
- Education and learning analytics: Tracking student engagement and performance to improve course design and support better learning outcomes.
- Operational optimization and equipment maintenance: Analyzing production and equipment performance data to reduce downtime, identify bottlenecks, and improve efficiency.
Further reading
FAQ
How does data mining differ from machine learning?
Data mining is the overall process of examining large datasets to uncover patterns, trends, and useful information. Machine learning is one of the main tools used within data mining. It provides the algorithms and models that help analyze the data, make predictions, or automate parts of the process.
What industries use data mining the most?
Data mining is widely used across industries such as finance, healthcare, marketing, cybersecurity, manufacturing, and human resources. For example, banks use it to detect fraud, retailers use it to analyze customer behavior to target marketing campaigns, healthcare organizations use it to improve diagnostics and treatment planning, and cybersecurity teams use it to monitor networks for unusual activity.
What are the main steps in the data mining process?
The main steps in the data mining process are defining the problem, collecting and preparing data, building models and mining patterns, and evaluating and interpreting results. These steps ensure that the analysis is focused, data is accurate, patterns are properly identified, and insights are actionable.
