Expressvpn Glossary
Digital footprint
A digital footprint, sometimes known as a digital shadow, is the trail of data created from internet users’ interactions with websites, internet services, applications, and other online platforms.
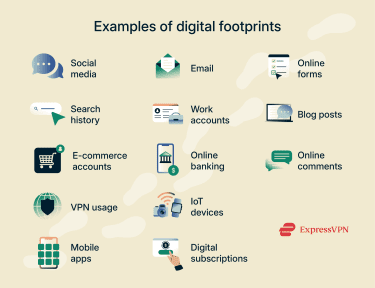
Examples of digital footprints
Here are some of the many ways internet users generate digital footprints:
- Social media activity: This includes social media interactions, likes, posts, comments, uploaded media, and friendship requests.
- Search history: Services like Google and YouTube typically retain information on keywords searched, average time spent on page, and content clicked or viewed.
- Online shopping behavior: Cookies can store data about e-commerce websites shoppers visit, products they look at, items added to cart, etc.
- Mobile app permissions: Mobile apps may collect device usage data, personal information entered into them, or data from other apps to which they have access.
- Metadata: Devices, apps, and online platforms collect metadata, which includes information automatically embedded in files such as photos, documents, or emails. This can reveal details like the date, time, device type, or even location where a file was created.
- Virtual private network (VPN) usage logs: Some VPN providers collect logs such as customers’ real IP addresses, connected server IP addresses, connection timestamps, websites visited, and content downloaded. For stronger privacy protection, it’s best to choose a reliable no-logs VPN that doesn’t store this information.
Why a digital footprint matters
Here are some of the ways a digital footprint may leave someone exposed:
- Doxxing: Disgruntled internet users can follow someone’s digital footprint to deanonymize them and leak sensitive personal information about them online.
- Targeted ads: Platforms like Facebook help marketers target users with specific ads based on websites they’ve visited, products they’ve looked at, etc.
- Data broker collections: Data brokers collect people’s digital footprints to build up a profile that they can sell to marketers, but this data could also leak to cybercriminals.
- Surveillance: A digital footprint may make it easier for a person’s routines, location, and habits to be tracked by third parties.
- Reputation risk: Posts, photos, or activity can affect personal or professional reputation. For example, digital footprints on websites like Ashley Madison ruined multiple reputations when they leaked.
Active vs. passive digital footprint
There are two common types of digital footprints:
- Active digital footprint: Created when users willingly share personal data, such as posting on social media or signing up for online accounts.
- Passive digital footprint: Created when data is collected without users’ awareness, such as IP addresses, device information, browsing activity, cookies, or browser fingerprints.
Active footprints are generally easier to control, while passive footprints are harder to manage because tracking happens in the background.
Further reading
- Private browser: Your best options for online privacy
- What is data privacy and why it matters: A complete guide
FAQ
Can I erase my digital footprint?
It’s impossible to entirely erase a digital footprint, often due to the limited control users have over where data appears and the presence of passive digital footprints. Instead, an active digital footprint can be reduced by closing social media accounts, deleting unused internet accounts, requesting online data removal, and avoiding sharing sensitive information online.
Is my digital footprint permanent?
Parts of a digital footprint can be permanent. Even if posts, accounts, or browsing data are deleted, copies may still exist on backup servers, in search engine caches, or in data collected by third parties. Information that’s been shared, saved, or reposted by others is especially difficult to remove completely. While reducing a footprint is possible, it’s nearly impossible to erase it entirely.
How does a VPN help reduce my digital footprint?
A VPN can’t prevent the creation of active digital footprints, like posts on social media or sign-ups for online accounts, but it can limit a passive digital footprint. By encrypting a user’s internet traffic and hiding their IP address, a VPN helps keep details like location and browsing activity private from websites, advertisers, and internet service providers (ISPs).
