Expressvpn Glossary
Network topology
What is network topology?
Network topology is the physical or logical layout that defines how devices (like computers, routers, and switches) are arranged and connected in a network. Its core purpose is to outline the structure of communication paths in a network.
How does network topology work?
Network topology works by organizing how devices (nodes) are physically connected and how data flows between them. There are two aspects to this:
- Physical topology: The layout of cables and hardware that defines how devices are linked.
- Logical topology: The path data takes when it flows through the physical network.
Physical and logical topologies sometimes align, but administrators can define data-sharing rules independently of physical layout.
Types of network topology
There are five primary network topology types:
- Bus topology: All devices connect to a single backbone cable (the bus). This simple design is cost-effective but vulnerable to single points of failure.
- Star topology: Each node connects to a central hub via dedicated cables, forming a star structure. Independent connections allow single-node removal without affecting the network. However, a central hub failure disables the entire network.
- Ring topology: Each node connects to two others in a circular loop, forming a closed path. Data usually travels in one direction, so if one device fails, the whole network can be disrupted. Bidirectional rings fix this by allowing data to flow both ways.
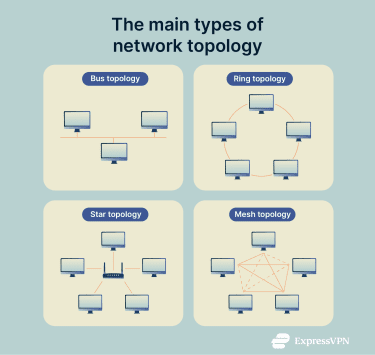
- Mesh topology: In a full mesh topology, every node connects to every other node, optimizing data transfer speed and eliminating single points of failure. There’s also a partial mesh topology option, where only selected nodes are directly connected.
- Hybrid topology: Combines multiple topologies for optimized cost, performance, and security. For example, several offices may use bus topologies internally but connect to a central hub or switch in a star topology, so failures in one office don’t affect the others. When these star networks are connected hierarchically, the overall design forms a tree topology, which is a common type of hybrid network in large organizations.
Why is network topology important?
Network topology impacts several key aspects of a network:
- Performance and reliability: The chosen topology affects data transfer speeds and how well the network handles failures.
- Scalability and maintenance costs: Topology affects how easily a network can be expanded or modified. For example, star topologies make it easier to add or remove devices without affecting the rest of the network.
- Communication efficiency: Mesh topologies improve speed and reliability through direct device-to-device connections.
- Identification of vulnerabilities and bottlenecks: A well-defined topology helps network administrators spot weak points, bottlenecks, or failure-prone areas early.
Where is network topology used?
Network topology applies to any environment with connected devices, including:
- Home and office networks: Topology helps organize how computers, printers, routers, and other devices connect and communicate.
- Data centers and enterprise IT infrastructure: Large-scale topologies ensure efficient data flow, high availability, and scalability across servers, storage, and network hardware.
- Telecommunications and internet service providers (ISPs): Topologies structure the flow of data across regional and global networks to support internet, phone, and media services.
- Internet of Things (IoT) and smart city systems: Network topology shapes how sensors, cameras, and connected devices share data across distributed locations.
Benefits and limitations
The benefits of network topology include:
- Structured design: Provides a clear layout for organizing and connecting devices efficiently.
- Easier troubleshooting: A defined topology makes it simpler to identify and isolate network issues.
- Optimized performance: Choosing the right topology can reduce congestion and improve data flow.
However, there are also limitations to consider:
- Cost: Some topologies, like mesh or hybrid, can be expensive to implement and maintain.
- Complexity: Larger or more advanced topologies require careful planning and skilled management.
- Single points of failure: Certain topologies (e.g., bus or star) are vulnerable if a central node or connection fails.
Further reading
FAQ
What is the difference between physical and logical topology?
Physical topology defines how devices are physically connected, while logical topology maps how data moves between them.
Which network topology is most common?
Star topology is the most common network topology in small home networks due to easy troubleshooting and scalability. However, other network types, such as wireless, Internet of Things (IoT), or wide area networks (WANs), often use mesh, hybrid, or other topologies.
What are the advantages of a mesh topology?
Mesh topologies eliminate single points of failure and maximize data transfer speed through direct node-to-node connections without central hubs.
How do I choose the right topology for my network?
The right topology depends on performance requirements and budget. For example, mesh topologies suit complex systems requiring high uptime, while star topologies offer simplicity and can be more cost-effective for small networks.
